주의! Caution!
해당 게시글은 Archive된 게시글 입니다.
Archive된 사유는 다음 중 하나에 해당 됩니다.
Archive된 사유는 다음 중 하나에 해당 됩니다.
- 작성 된지 너무 오랜 시간이 경과 하여, API가 변경 되었을 가능성이 높은 경우
- 주인장의 Data Engineering으로의 변경으로 질문의 답변이 어려워진 경우
- 글의 퀄리티가 좋지 않아 글을 다시 작성 할 필요가 있을 경우
Pytorch 에서는 CNN과 마찬가지로, RNN과 관련 된 API를 제공합니다. 이를 이용해 손쉽게 RNN 네트워크를 구축 할 수 있습니다.
Recurrent Neural Network
RNN (Recurrent Neural Network)를 위한 API는 torch.nn.RNN(*args, **kwargs) 입니다.
일단 Input 시퀀스의 각 요소에 대해, 각 레이어에서는 다음 연산을 수행합니다.
Parameters
input_size:Input의 사이즈에 해당 하는 수를 입력하면 됩니다.hidden_size: 은닉층의 사이즈에 해당 하는 수를 입력하면 됩니다.num_layers:RNN의 은닉층 레이어 갯수를 나타냅니다. 기본 값은 1입니다.nonlinearity: 비선형 활성화 함수를 선택합니다.tanh,relu중 하나를 선택 가능하며, 기본 값은tanh입니다.bias: 바이어스 값 활성화 여부를 선택합니다. 기본 값은True입니다.batch_first:True일 시,Output값의 사이즈는 (batch, seq, feature) 가 됩니다. 기본 값은False입니다.dropout: 드롭아웃 비율을 설정 합니다. 기본 값은 0입니다.bidirectional:True일 시, 양방향 RNN이 됩니다. 기본 값은False입니다.
num_layers가 2라면?
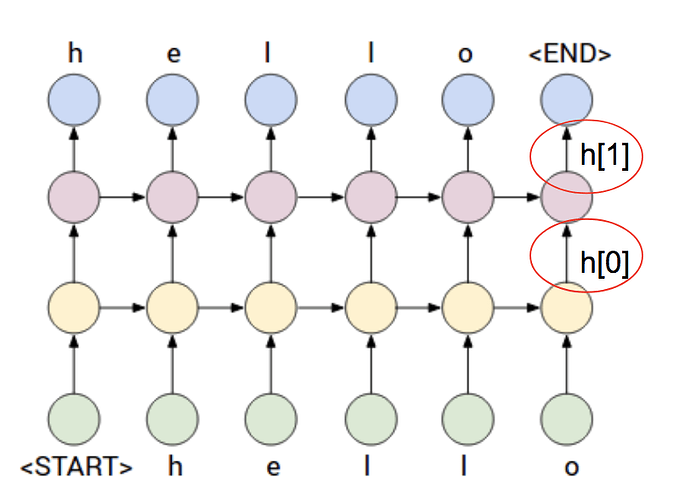
다음 그림과 같은 신경망이 만들어 진다고 생각 하면 됩니다.
Inputs: input, h_0 (tuple 형태)
input: (seq_len, batch, input_size)h_0: (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size) 여기서bidirectional이True라면,num_directions는 2,False라면 1이 됩니다.
Outputs: output, h_n (tuple 형태)
output: (seq_len, batch, num_directions * hidden_size) 여기서bidirectional이True라면,num_directions는 2,False라면 1이 됩니다.h_n: (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size) 여기서bidirectional이True라면,num_directions는 2,False라면 1이 됩니다.
Code Example (Natural Language Processing)
해당 코드는 NLP (Natural Language Processing)을 위한 코드입니다. 앞의 두 단어를 보고, 뒤에 나올 단어를 예측 합니다.
- In
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
sentences = ["i like dog", "i love coffee", "i hate milk", "you like cat", "you love milk", "you hate coffee"]
dtype = torch.float
"""
Word Processing
"""
word_list = list(set(" ".join(sentences).split()))
word_dict = {w: i for i, w in enumerate(word_list)}
number_dict = {i: w for i, w in enumerate(word_list)}
n_class = len(word_dict)
"""
TextRNN Parameter
"""
batch_size = len(sentences)
n_step = 2 # 학습 하려고 하는 문장의 길이 - 1
n_hidden = 5 # 은닉층 사이즈
def make_batch(sentences):
input_batch = []
target_batch = []
for sen in sentences:
word = sen.split()
input = [word_dict[n] for n in word[:-1]]
target = word_dict[word[-1]]
input_batch.append(np.eye(n_class)[input]) # One-Hot Encoding
target_batch.append(target)
return input_batch, target_batch
input_batch, target_batch = make_batch(sentences)
input_batch = torch.tensor(input_batch, dtype=torch.float32, requires_grad=True)
target_batch = torch.tensor(target_batch, dtype=torch.int64)
"""
TextRNN
"""
class TextRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(TextRNN, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=n_class, hidden_size=n_hidden, dropout=0.3)
self.W = nn.Parameter(torch.randn([n_hidden, n_class]).type(dtype))
self.b = nn.Parameter(torch.randn([n_class]).type(dtype))
self.Softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, hidden, X):
X = X.transpose(0, 1)
outputs, hidden = self.rnn(X, hidden)
outputs = outputs[-1] # 최종 예측 Hidden Layer
model = torch.mm(outputs, self.W) + self.b # 최종 예측 최종 출력 층
return model
"""
Training
"""
model = TextRNN()
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
for epoch in range(500):
hidden = torch.zeros(1, batch_size, n_hidden, requires_grad=True)
output = model(hidden, input_batch)
loss = criterion(output, target_batch)
if (epoch + 1) % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.6f}'.format(loss))
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
input = [sen.split()[:2] for sen in sentences]
hidden = torch.zeros(1, batch_size, n_hidden, requires_grad=True)
predict = model(hidden, input_batch).data.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
print([sen.split()[:2] for sen in sentences], '->', [number_dict[n.item()] for n in predict.squeeze()])- Out
Epoch: 0100 cost = 0.409607
Epoch: 0200 cost = 0.099554
Epoch: 0300 cost = 0.027191
Epoch: 0400 cost = 0.013870
Epoch: 0500 cost = 0.008780
[['i', 'like'], ['i', 'love'], ['i', 'hate'], ['you', 'like'], ['you', 'love'], ['you', 'hate']] -> ['dog', 'coffee', 'milk', 'cat', 'milk', 'coffee']Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory)를 위한 API는 torch.nn.LSTM(*args, **kwargs) 입니다. LSTM은 기울기 폭발, 기울기 소실 등의 문제를 해결 하기 위해 기존 RNN을 개선한 구조로, Input 시퀀스의 각 요소에 대해, 각 레이어에서는 다음 연산을 수행합니다.
Parameters (RNN과 비슷합니다.)
input_size:Input의 사이즈에 해당 하는 수를 입력하면 됩니다.hidden_size: 은닉층의 사이즈에 해당 하는 수를 입력하면 됩니다.num_layers:RNN의 은닉층 레이어 갯수를 나타냅니다. 기본 값은 1입니다.bias: 바이어스 값 활성화 여부를 선택합니다. 기본 값은True입니다.batch_first:True일 시,Output값의 사이즈는 (batch, seq, feature) 가 됩니다. 기본 값은False입니다.dropout: 드롭아웃 비율을 설정 합니다. 기본 값은 0입니다.bidirectional:True일 시, 양방향 RNN이 됩니다. 기본 값은False입니다.
Inputs: input, (h_0, c_0) (tuple 형태)
input: (seq_len, batch, input_size)h_0: (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size) 여기서bidirectional이True라면,num_directions는 2,False라면 1이 됩니다.c_0: (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size) 초기 Cell State 입니다.
만약 (h_0, c_0)이 없다면, 기본 값은 영벡터 입니다.
Outputs: output, (h_n, c_0) (tuple 형태)
output: (seq_len, batch, num_directions * hidden_size) 여기서bidirectional이True라면,num_directions는 2,False라면 1이 됩니다.h_n: (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size) 여기서bidirectional이True라면,num_directions는 2,False라면 1이 됩니다.c_n: (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size) Cell State 입니다.
Code Example
해당 코드는 NLP (Natural Language Processing)을 위한 코드입니다. 앞의 두 단어를 보고, 뒤에 나올 단어를 예측 합니다. CNN 코드와는 Input 파라미터에 차이가 있습니다.
- In
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
sentences = ["i like dog", "i love coffee", "i hate milk", "you like cat", "you love milk", "you hate coffee"]
dtype = torch.float
"""
Word Processing
"""
word_list = list(set(" ".join(sentences).split()))
word_dict = {w: i for i, w in enumerate(word_list)}
number_dict = {i: w for i, w in enumerate(word_list)}
n_class = len(word_dict)
"""
TextRNN Parameter
"""
batch_size = len(sentences)
n_step = 2 # 학습 하려고 하는 문장의 길이 - 1
n_hidden = 5 # 은닉층 사이즈
def make_batch(sentences):
input_batch = []
target_batch = []
for sen in sentences:
word = sen.split()
input = [word_dict[n] for n in word[:-1]]
target = word_dict[word[-1]]
input_batch.append(np.eye(n_class)[input]) # One-Hot Encoding
target_batch.append(target)
return input_batch, target_batch
input_batch, target_batch = make_batch(sentences)
input_batch = torch.tensor(input_batch, dtype=torch.float32, requires_grad=True)
target_batch = torch.tensor(target_batch, dtype=torch.int64)
"""
TextLSTM
"""
class TextLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(TextLSTM, self).__init__()
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=n_class, hidden_size=n_hidden, dropout=0.3)
self.W = nn.Parameter(torch.randn([n_hidden, n_class]).type(dtype))
self.b = nn.Parameter(torch.randn([n_class]).type(dtype))
self.Softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, hidden_and_cell, X):
X = X.transpose(0, 1)
outputs, hidden = self.lstm(X, hidden_and_cell)
outputs = outputs[-1] # 최종 예측 Hidden Layer
model = torch.mm(outputs, self.W) + self.b # 최종 예측 최종 출력 층
return model
"""
Training
"""
model = TextLSTM()
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
for epoch in range(500):
hidden = torch.zeros(1, batch_size, n_hidden, requires_grad=True)
cell = torch.zeros(1, batch_size, n_hidden, requires_grad=True)
output = model((hidden, cell), input_batch)
loss = criterion(output, target_batch)
if (epoch + 1) % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.6f}'.format(loss))
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
input = [sen.split()[:2] for sen in sentences]
hidden = torch.zeros(1, batch_size, n_hidden, requires_grad=True)
cell = torch.zeros(1, batch_size, n_hidden, requires_grad=True)
predict = model((hidden, cell), input_batch).data.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
print([sen.split()[:2] for sen in sentences], '->', [number_dict[n.item()] for n in predict.squeeze()])- Out
Epoch: 0100 cost = 0.301909
Epoch: 0200 cost = 0.039160
Epoch: 0300 cost = 0.017456
Epoch: 0400 cost = 0.009996
Epoch: 0500 cost = 0.006636
[['i', 'like'], ['i', 'love'], ['i', 'hate'], ['you', 'like'], ['you', 'love'], ['you', 'hate']] -> ['dog', 'coffee', 'milk', 'cat', 'milk', 'coffee']마치며
다음 시간부터는 Pytorch를 이용해서 실제 동작하는 어플리케이션 을 만들어 보도록 하겠습니다.
References
Pytorch Basic 시리즈의 다른 글
2020-04-26
2020-04-19
2020-04-08
2020-04-04
2020-03-28
2020-03-23
Recent Posts in Deep-Learning Category